Conducting a technical SEO audit is essential to any successful SEO strategy. By regularly assessing and improving the technical elements of your website, you can increase visibility in search engine results and drive more organic traffic to your site.

Businesses need to pay more attention to regularly auditing their online presence.
In this guide, I cover how to do a technical SEO audit in just ten steps effectively. I’ll discuss how to analyze your website, identify technical issues, and develop solutions or recommendations.
Table of Contents[Hide][Show]
- What are the likely reasons for a technical SEO audit?
How to do the Technical SEO Audit, step by step+−
- Step 1: Perform manual checks
- Step 2: Crawl the website and start the analysis
- Step 3: Review Google Search Console and Analytics
- Step 4: Identify Problems With Crawlability and Indexation
- Step 5: Review On-Page Elements
- Step 6: Image Optimization
- Step 7: Dig Deeper into Internal Links
- Step 8: Review External Links
- Step 9: Analyze Page Performance and Site Speed
- Step 10: Run a parallel Javascript-enabled crawl
- Wrapping Up
What Is an SEO Audit?
SEO audits are periodic reviews of a website to assess its search engine rankings’ overall health and performance.
During an SEO audit, experts analyze the website’s architecture, content quality, technical elements, and other factors to identify opportunities for improvement.
SEO audits are a necessary part of any well-rounded SEO strategy. Without it, website owners may miss opportunities to increase their organic search visibility and performance.
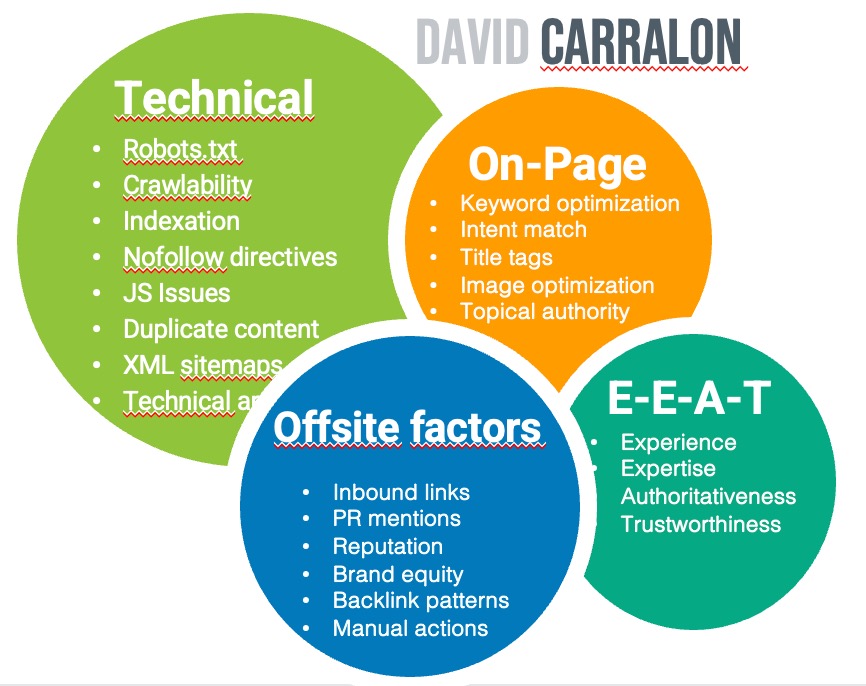
The three main aspects of an SEO audit are technical, content, and links.
So what is a technical SEO Audit, then?
A technical SEO audit identifies and prioritizes the technical issues holding your website back from achieving its desired ranking in search engine results. Addressing and optimizing these areas can improve your SEO performance and drive more organic traffic to your website. The concept of ‘technical’ can be interpreted in many different ways.
I do not consider title tags, content optimization, or meta descriptions part of a technical SEO audit. Still, the client often requests these, so I add them to my study.
Regarding offsite factors, I do not consider backlinks analysis as part of a technical SEO audit either. However, if the client requests a backlink audit on suspicion of some manual penalty, I also bring in the link portfolio audit as part of the technical SEO audit.
It really depends!
Moreover, a technical SEO audit should focus on the technical elements of a website, even if some aspects overlap with On-page or off-page SEO.
What are the likely reasons for a technical SEO audit?
There are some common reasons why a technical SEO audit may be needed:
- The marketing team may need to identify any technical issues or roadblocks that may have popped up as part of an internal project.
- you are launching a new website or making significant changes to your existing website and may want a 2nd opinion on specific developments.
- Your company’s web presence is about to expand internationally either by targeting regions or languages, and you need an audit on compliance, opportunities or simply for reassurance
- traffic suddenly drops or on a downward trend with no apparent reason
- The website moves from a lamp environment onto React, and your team needs support
- The website’s organic traffic has plateaued
- You would like a second opinion from a technical SEO Consultant
- Your team has completed the migration of the website, and something has gone wrong
Running a technical SEO audit before and after the changes is a good idea. It ensures that you don’t miss any significant opportunities for improvement.
Before You Begin
Before you begin your technical SEO audit, let’s look at what you need to have in place.
Search and Traffic Analytics
If you plan to perform a paid audit for a client or do it in-house, at the bare minimum, you will need access to Google Search Console but, ideally, Google Analytics too.
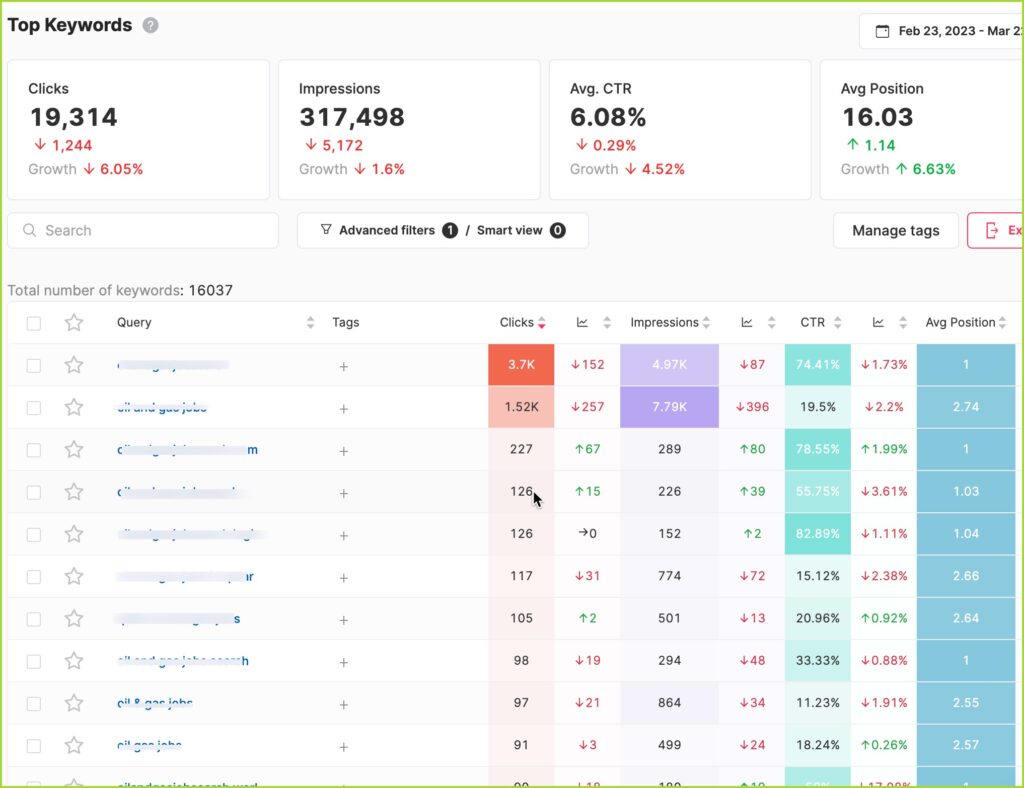
I rarely accept requests to perform a technical SEO audit without having access to GSC first. I like to explain to the client why the data in GSC is critical to validate the diagnosis of errors, problems, and even manual penalties.
Keyword rankings/positioning reports
Rankings can be obtained via Google Search consoles, however,, having access to your client’s search engine ranking history is a bonus.
This is often a luxury when you do get it as many businesses do not track search engine rankings at all.
You can use tools to assess drastic fluctuations in target keyword positions, such as SEMrush, SE Ranking, or Sistrix.
I always ask for information on redirects as it helps get access to how these critical tasks may have been handled in the case of migration that has gone wrong and the expected subsequent traffic drop.
Link building lists
If you are conducting an audit that includes checking out the backlink portfolio and building up a disavow file to submit, then make sure you ask for a list of backlinks they may have been sourcing in recent months or whichever period applies.
You may be surprised how many people who have been buying links do have these backlink lists. This makes the process much easier as a possible manual action or algorithmic penalty can be traced more easily. It makes the cost of the SEO audit cheaper too.
Website client brief
When you get contacted by a potential client, there are so many pieces of information you need to perform technical SEO audits effectively. You must set up a system to collect all this information properly to save time.
I suggest you create a project brief document that you can hand out to the client to collect essential information from the client easily. If you are reading this as an inhouse SEO then this shouldn’t apply much to you as you are supposed to know the strategy, moves and goals behind the website you manage.
This brief should include questions such as:
- website’s history
- current performance
- recent website migrations or rebranding
- close competitors
- target market
- website goals for SEO or overall website goals
- recent changes effected on the website
- recent issues, drops, or tech having gone wrong
- possible upgrades pushed out by other teams, eg: UX, CRO
- Any specific areas to focus the technical audit on.
Once you have all this information, you have an excellent baseline to perform the audit efficiently.
How to do the Technical SEO Audit, step by step
Now, let’s look at the ten steps to help you conduct a successful technical SEO audit.
Step 1: Perform manual checks
Manual analysis is an incredible way to get first-hand tips on what could be wrong with the website.
It does help to navigate the website as a user and become familiar with it: click over navigation items, categories, and subcategories, apply filters if it’s an e-commerce site, do internal searches, identify template flaws… make sure you take notes for anything that looks odd.
Use Chrome SEO extensions
You will continue the analysis, but this time with your auditor hat on, open up the various browser ‘developer’ extensions you may have, switch off CSS, javascript and look at what’s visible.
Do the same thing with SEO Chrome extensions. eg: SEO minion, Detailed, Link Redirect Trace…
Robots.txt configuration
Check out the robots file and see what’s disallowed, see if the sitemap is listed, then go and check if there is anything odd about it.
Manually check indexation.

Then run a manual site: operator check and see how much content Google gives you back as indexed. Don’t take this information at face value; compare it with the data in GSC, and wait for the first crawl to start drawing out various hypotheses that you will later put to the test.
Manually check mobile friendliness.
Check the website usability on your smartphone. This mobile-friendly manual review can be later contrasted with a proper mobile-friendly test. Google grants preference to mobile-friendly websites, and for a good reason.
According to Statista, one-third of United States internet users make weekly purchases from their mobile phones, so it is worth a manual check of the website on your smartphone/s.
Asses the different website templates
A manual review involves reviewing the different templates of a website and assessing it for potential SEO issues. It includes checking the page title, meta description, schema build-up, URL structure, content quality, and other factors.
This process can be highly time-consuming but can further ensure that the content gets audited rightly, and everything will make more sense once you start crawling the website and match each content type visually to each template. Take notes and even print out the most important templates. It will help you throughout the full analysis.
Manual webpage auditing is excellent for carefully assessing how the different website templates are designed or built, but of course, to properly audit and identify issues in bulk, there is nothing like a full crawl of the website.
Step 2: Crawl the website and start the analysis
The first step is to crawl your website with your preferred tool.
I usually spend the necessary time to configure these five at the bare minimum:
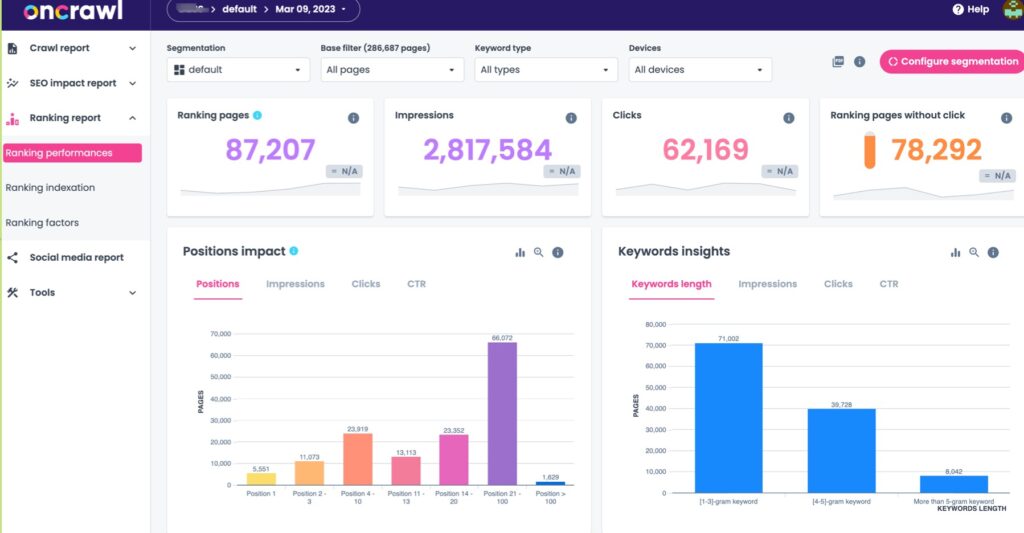
- Screaming frog, desktop-based crawler
- Sitebulb, desktop-based audit tool
- Oncrawl, cloud-based crawling tool
- Ahrefs, cloud-based crawling tool
- SEOcrawl.com, for GSC visualisations
These initial crawls will help you get an overall view of the website and identify any problems with your SEO.
Once the initial crawl is completed, check the data to ensure you complete the configuration. Ensure the crawls are integrating GSC, GA or Ahrefs or Majestic data via their APIs.
On the cloud-based crawling tools, you now have the chance to configure the page types and different website sections. This may feel like a lot of work, especially for small website audits, but I always do it as it saves me time later with understanding where issues stem from or where bottlenecks exist.
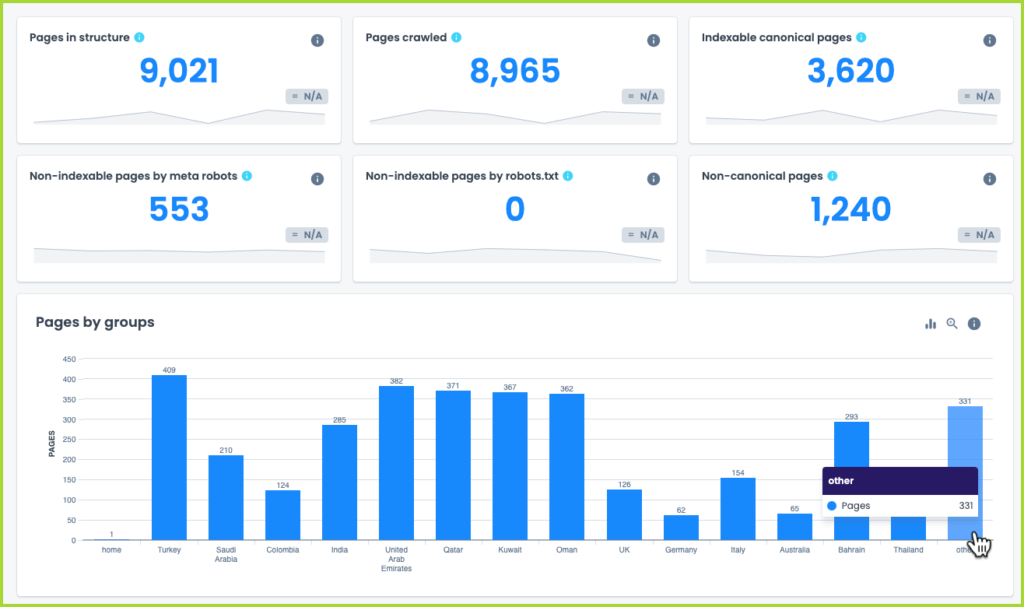
The actual crawl may typically run for about 30 mins, if it’s a small website, and up to 2-3 days, for large websites and depending on how fast the crawler is able to crawl without bringing down the server.
Do not go to aggressive on the crawler speed, even if you have been granted GSC permissions because the devops teams may end up blocking the robots used by different crawling tools.
Once the audit reports are ready, the challenge is to know exactly where to look to find the golden nuggets. If the client has been clear on what is wrong with the website, it is easier to prioritize the analysis. If that’s not the case, the goal is broader as all areas would need to be addressed to help you prioritize the areas of your website that could be negatively impacting your site.
I usually like to take a good look across the entire crawl reports on each crawl tool, take notes, and then narrow down the issues to the biggest ones estimated to bring the best results if they were solved.
Here are some of the things to look out for :
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content is a common issue that can negatively impact your website’s rankings. Duplicate content means that the same content is showing up on multiple pages of your website. Make sure to identify any duplicate content and fix it quickly. A great example is two blog posts about similar topics with the same points and keywords.
Crawlability Issues
Have all parts of the website been crawled? Is there any part of the website reported as ‘not crawled’ that you think it should be? watch out for nofollow content and content that’s blocked out in the robots file, eg: pagination URLs are often either canonicalised to the front of roboted out.
If there are key areas of the website that should have been crawled, but aren’t, you then have some hints and you should dig in deeper.
Crawl Errors
Crawl errors are another common issue that can affect your website’s performance. If a crawl error occurs, the website is not loading correctly or sending out the wrong HTTP, then that’s worth digging into.
Multiple 302 redirects ending in a 404 page as the final destination is a common issue I find in large website throughout my audits.
Broken Links or 404 errors
Broken links can have a significant impact on your website’s performance. Broken links can occur due to coding errors, dead pages, or website redesigns. It can be worse if you have a chained redirect that ends in a non-existing page, so the chain redirect of 301 or 302 ends in 404, 410, or the like. See a full section on this further down the page
Active vs inactive pages
This kind of insight can be an eye-opener for most business owners because everyone tends to keep content that either serves no purpose, is decommissioned but forgotten, becomes an orphan, or forgets about it.
Large sways of stale content is always detrimental for SEO.
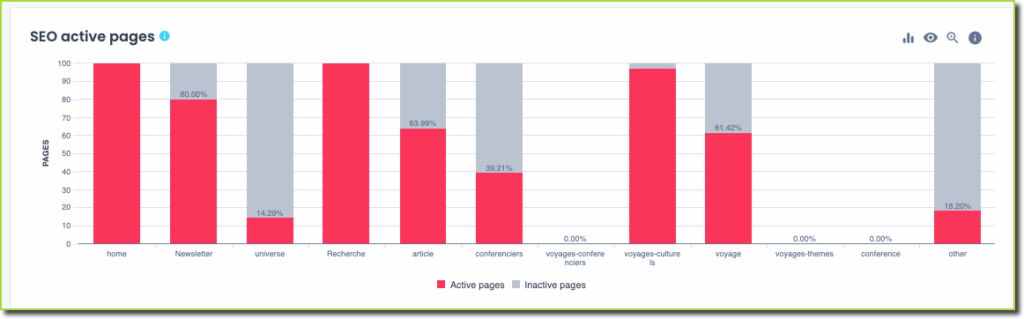
Active meaning pulling in at least 1 SEO visit to the website. Inactive means pages that do not atract any organic traffic at all.
It is not uncommon to find websites where, following a crawl, one becomes aware that only a 10% of the website content actually delivers organic traffic, and less than 2-5 % actually converts either by generating sales or leads for the company.
Missing or duplicated critical SEO Tags
Meta tags tell search engines vital information about all your pages, such as how they should display in search queries.
Ensure your website uses the correct meta tags, such as title and description. It can seriously impact your website’s performance. It is vital to make sure that they are all present and correct.
It is common to find duplicated title tags or H1s, especially on e-commerce websites.
All crawl errors flagged by SEO Tools should be manually checked on the website code source and page content or cross-checked with other tools’ reports to validate potential issues.
Step 3: Review Google Search Console and Analytics
Once you thoroughly understand your audit results, the next step is to review the Google Search Console and Analytics data individually. Although this data is crunched with the crawl data, provided you have added their APIs to the crawls, it is still worth reviewing the GSC and GA separately.
Google Search Console helps you identify any issues with your website’s SEO. You can use the Search Console to identify any crawl errors, broken links, or other problems affecting your website’s performance.
Google Analytics provides in-depth insights into how users interact with your website, including the number of visits, total time spent, and user conversion rates. This data can help you identify issues with your website’s user experience and make adjustments to improve it.
These programs aim to gain insight into user behavior impacting your SEO performance. Specifically, check for changes in search rankings, impressions, clicks, and other metrics that might indicate an issue.
Additionally, you can review any errors or warnings from the Search Console to see if any urgent technical issues need to exist. For example, if your site is not loading correctly or returning a 404 error, you will want to find out the cause and fix it as soon as possible.
Lastly, by reviewing analytics data, you can identify any potential issues with website usability or user experience. It may include low click-through, high bounce rates, or slow page speed.
Once you have identified any potential issues, prioritize them and create a plan to address them. Start with updating changes to the website code if need be. Then focus on creating an SEO strategy. The images are included in the SEO strategy. For example, you may need to update the picture by selecting a different image with new ALT text and dimensions.
The goal here is to compare your Google notes with the notes from the audit. At this point, you’ll have a complete picture of your website’s performance. You can begin implementing the changes necessary to improve it.
Step 4: Identify Problems With Crawlability and Indexation
So how are crawlability and indexation working together?
Crawlability is the process by which search engine bots succeed (or not) at finding and crawling every critical webpage within a website. Indexability, in turn, is the ability for a web page to be indexed once it has been crawled.
If a page is not accessible for whatever reason, it will not be indexed and will not appear in the search engine results. However, a webpage can be easily crawled and still not indexed by search engines. During the technical SEO audit, you must determine why crawlability and/or indexability fail.
It is essential to assess both indexation and crawlability when performing an SEO audit.
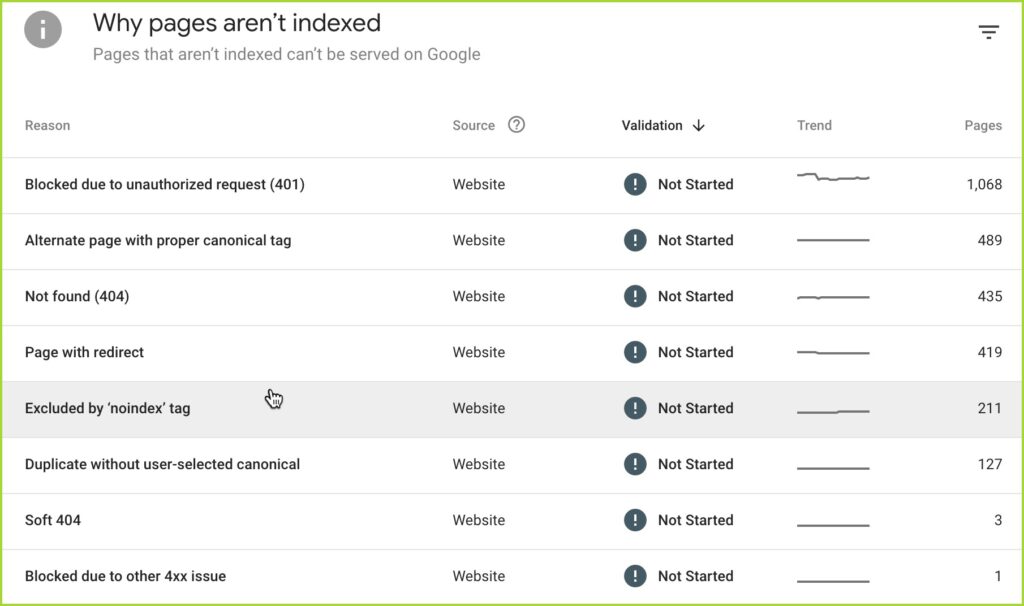
To do this, you can use Screaming Frog SEO Spider to identify any potential crawl errors. Then use Google Search Console to check for any indexation issues. Additionally, you can use specialized tools
If you find any indexation or crawlability issues, note them and determine the cause. Some of the most notorious crawlability issues involve
- numerous counts of broken links,
- solving rendering on javascript-powered websites,
- incomplete or deficient XML sitemaps
- unsuitable or patchy internal linking
- bad information architecture
- incorrect us of the robots.txt file where specific URLs are blocked from crawling
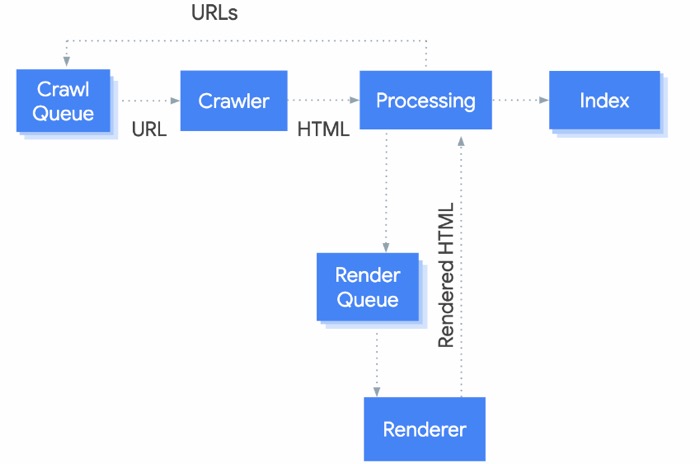
Note: if the site being audited runs on javascript, the paradigm ‘Crawling-indexation’ becomes ‘Crawling-indexation and Rendering’
How to Fix Broken Links
When it comes to technical SEO, broken links are a major issue. If search engine bots can’t access a page, they won’t be able to index it. It can drastically reduce your website’s visibility in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Set time aside to track all the internal links on the website and identify areas of the site or specific content types that may not be getting as much internal link equity as others. This is an essential on technical SEO audits as it allows you to identify and prioritize the issues hindering your website’s performance.
By now, you should have a list of broken links from your site audit and Google Console and Analytics research. Broken links result from various factors, such as outdated URLs or URLs that have gotten deleted from the website. Your options for fixing broken links are removing them entirely or replacing them with a valid link.
Audit XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is an essential part of a technical SEO audit. It is a special file that tells search engine bots which pages to crawl and index, making it easier for them to find your site.
To audit the XML sitemap, you can use Google Search Console. Once in your dashboard, click on sitemaps on the left sidebar and then click on ‘Add/Test Sitemap’. Enter your sitemap URL, and Google will begin to crawl it, and soon give you a report. The goal, amongst other things, is to ensure that :
every URL in your sitemap is critical to you website
only have compliant URLs in your sitemap (HTML format, 200HTTP, self-canonical URLs)
every URL is linked to the website structure
Every URL in you sitemap should therefore be crawled, indexed and ideally ranked. If one of those three conditions are not met, dig in and find out why. The journey into auditing XML sitemaps often takes you into a deep and complicated rabbit hole.
Always question why there are urls/pages that are indexed and possibly ranking but not have a present in the sitemap group. Every page critical to the business should be in the XML sitemap.
Creating Robots.txt Files
Robots.txt is a text file that commands search engine bots on which pages to avoid crawling and indexing on your website. It can be useful if you have pages you want to avoid being visible in the SERPs. For example, if you have a page with sensitive information or duplicate content, you can use a robots.txt file to block it from being indexed.
To create a robots.txt file, you will add code to a light text file that can be created in notepad. Once you have added the code, upload it to your website’s root directory.
Consider this entire step one of the most important ones in your SEO audit, as any issues with indexation and crawlability will severely limit the visibility of your website in the search engine results.
Check duplication at platform-level
Identical content under the same domain but a different domain protocol is common.
Eg: https://fastbullettrain.com/category/url1 and
http://fastbullettrain.com/category/url1 both could resolve and return HTTP 200
The same issue is common between www and non-www versions of the domain.
When that happens, content is duplicated and reused across different URL versions. This can potentially dilute link equity and confuse users and Google, who may use the wrong canonical version of your domain.
Step 5: Review On-Page Elements
The on-page elements we’re referring to are:
- Page titles and tags
- Meta descriptions
- Data Structure
- Canonical Tags
- Hreflang tags
A website’s on-page elements will tell search engine bots what the page is about and how relevant it is to users’ queries.
When performing an SEO audit, you should benchmark every element against recommended standards and flag that on the report. For example, title tags should be unique, not too long or too short, and contain the target keyword. Likewise for meta descriptions: unique, descriptive, and under 150 characters long.
Additionally if the audit is about Internationalisation, do check for compliance on the following area:
- correct us of language use on page
- appropriate use of Hreflang and their syntax ( not an easy one)
- potential conflicts with canonical tags (this is a common issue)
While the canonical tag tells Google which page version is the original and prevents duplicate content issues, the hreflang tag indicates to search engine bots the language used on a page and the intended region.
The truth is that multiple sites in your network can have articles on the same topic, with all of them providing value to their readers in different geographic locations. That’s why canonical tags and hreflang tags are essential for international SEO. The most minor mistakes here can majorly affect your site’s visibility.
By adding these elements to your site, you will help search engine bots understand the relevance of your pages to the users’ queries in each geographical location.
Step 6: Image Optimization
Images have become an essential part of SEO, as they can provide users with visual cues that make consuming content easier. But it’s not just the visuals that matter. Image optimization with the right size, file type, and ALT attributes can also help your search engine rankings.
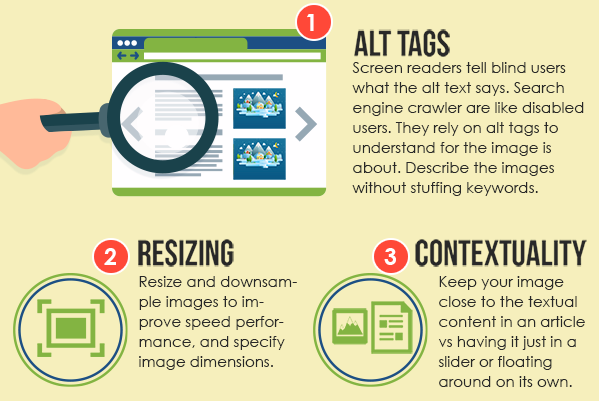

Image issues will show up in your audit. The main errors you’ll see are page speed issues, incorrect image size, broken images, and missing ALT text.
Site Speed Issues
The size of images is essential when it comes to speed. If your image files are too large, they will take longer to load, affecting your website’s overall performance. They should not be too small if they want to stand a chance to rank.
Ensure all images used on your site are compressed and not too big. You can use TinyPNG or CompressJPEG for effective compression and resizing.
Incorrect Image Size
When using images on a website, it’s essential to ensure they are correctly sized. If an image is too small or too large, it will look terrible on your website. If the image size isn’t true or causes the image to be blurry or distorted, you increase the chance of losing readers.
You should also specify image size using html.
Broken Images (404s)
Broken images are another common issue when performing an SEO site audit. A broken image is an image that fails to load on the page. A dead link, broken code, or incorrect file type can cause it.
When a broken image pops up, the skeleton of the photo will show up, but it won’t load the picture. Your goal is is to look for patterns that help you work out what has broken up specific groups of images, eg: a recent website migration where images were not taken into account and adequately redirected, much like pages urls.
Missing ALT Text
ALT text or alternative text is a way to provide search engine bots with additional information about an image. ALT text should be descriptive and contain the target keyword. It will help search engine bots better understand the content on your page and increase its relevance to users’ queries.
File Types and Free Images
Finally, ensure you’re using suitable file types for your images. JPGs and PNGs generally work the best for photos, as they have smaller file sizes than other formats. PNG is recommended for logos and other sharp graphics, while JPEG is best for photos and other pictures with great detail.
As you optimize and compress all images, your website’s performance will improve too.
Step 7: Dig Deeper into Internal Links
Internal links are one of the most underrated elements in SEO. They are links that point from one page to another on the same website.
Ae you wondering why a specific segment within a client website is performing poorly and hardly getting any organic traffic? check out the internal linking report on your favorite SEO tool and you may be surprised with the findings:
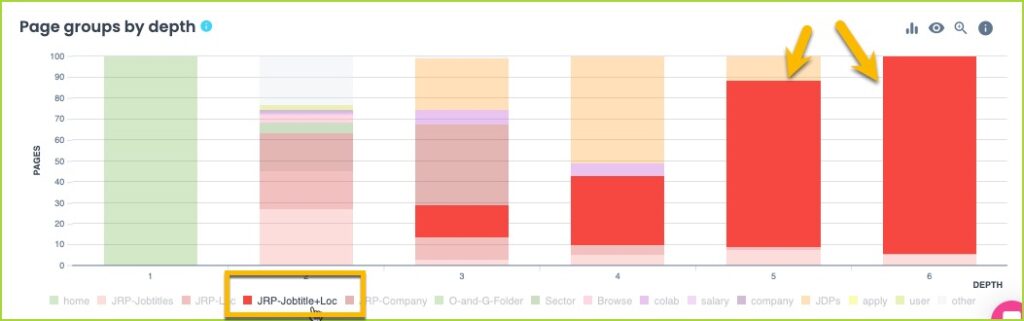
Internal linking is crucial because :
- it helps search engine bots crawl your website and understands each page’s content.
- it allows you to share link equity across pages, which can help improve your search engine rankings.
- it will enable you to leverage the power of your website’s authority
- you can effectively send traffic from a high-ranking page to a low-ranking page
It can have a favorable effect on the overall SEO of your website. This is why it must be considered highly during a technical SEO audit.
These are some of the things to look at
- Links should be coded in html. Javascript intenal links are not advisable.
- Excessive chained redirects
- Unnecessary redirects
- Links should be easy to find and clearly visible on the page.
- Links should also be descriptive to help understand the content of the pages they are linking to.
- Odd use of ‘nofollow’ in specific segments
- Ensure most internal links, supposed to be permanent, are 301 http
- broken internal links returning 404 HTTP. These lead to a poor user experience, hurting your search engine rankings.
Step 8: Review External Links
Now, let’s talk about external links; backlinks. These point from one website to another. They are essential for SEO because they help search engine bots find your content and credit it with a vote of confidence.
When performing an SEO site audit, you should review the external links on your website and make sure:
- that they are working properly. Broken external links can lead to a poor user experience, and wasted link equity
- Are external links relevant to the content they are linking to, or you spot many unrelated or spammy links.
- Is there a healthy balance between ‘dofollow’ and ‘nofollow’ backlinks?
- Can you spot patterns of shady backlink practices?
External links need more monitoring than internal links, as you do not have control over the content on the outer pages. You should periodically check to ensure the external links are still working and the linked page’s content is relevant and valuable to your readers.
Finally, one important thing to remember with external links is that they can be seen as endorsements by search engines. If you link to a low-quality website, it could hurt your domain authority and search engine rankings. Only link to reputable websites and sources to ensure your website remains in good standing with search engines.
The overall goal is to avoid creating dead-end articles with your content. The longer you keep your visitors on your website, the more likely they will convert into leads or sales.
You want engaged readers that click on your site, absorb your content, read and click on the ads, and search your site for the solution to their problem. You can keep your visitors engaged and interested with comprehensive and thoughtful links (internal and external links).
Step 9: Analyze Page Performance and Site Speed
Sadly, even if readers love your content, they will grow weary of dealing with slow loading time and may leave your site before they can absorb the information.
Imagine being on your lunch break and needing to order online, but the site keeps crashing. You’d be so frustrated that you would leave the site and go elsewhere. The same is valid for visitors to your website. They won’t stick around to read your content if it takes too long for the page to load.
Since July 2018, Google has looked at your mobile page speed and used that as a ranking factor for organic search engine rankings. If you want to rank higher, you’ll need a fast-loading website.
Analyzing page performance is critical, affecting the user experience and search engine rankings.
When looking at page performance and site speed as part of your SEO site audit, make sure you analyze the following metrics:
Page Load Time
As mentioned earlier, you want your pages to load quickly for desktop and mobile devices. The longer your page takes the load, the higher the risk of your reader going elsewhere.
Server Response Time
If your server is slow to respond, it can lead to a poor user experience. Have you ever looked at a website, and because it took so long to load, you got a message saying that the server didn’t respond? Usually, when this happens, you must keep refreshing to load the page.
Image Weight
Large images take longer to download and can slow your website down. We mention image optimization again because they are crucial to page performance.
Page Size
Pages must be optimized for speed, meaning images and other elements get compressed but not distorted to enhance page performance. The more pictures and videos you add to your webpage, the bigger it gets and the slower it will load.
Core Web Vitals
HTML/CSS Validation
Errors in your HTML or CSS can slow down page load time. A mistake in your HTML or CSS means the browser has to work harder, which can slow down page load time.
Your goal is to work hand in hand with Google. All Google wants to do is keep more people on the web and spend more time on each page. They want to increase user experience.
By now, you should see a trend in what you should focus on when doing a technical SEO site audit. You want to ensure that your website is designed for speed, optimized for performance, and has well-structured, engaging, and relevant content. If you pay attention to these things consistently, you will be on a consistent path to ultimate performance and evolution.
Step 10: Run a parallel Javascript-enabled crawl
This step will only be needed if you deal with javascript-powered websites such as NextJS, AngularJS, or others.
You may have asked the site owner if the site runs on javascript, and you may have been told that server-side rendering is running for every webpage, but experience tells me never to take that as a confirmation of a fact.
Running a 2nd crawl with javascript enabled may reveal some valuable points.
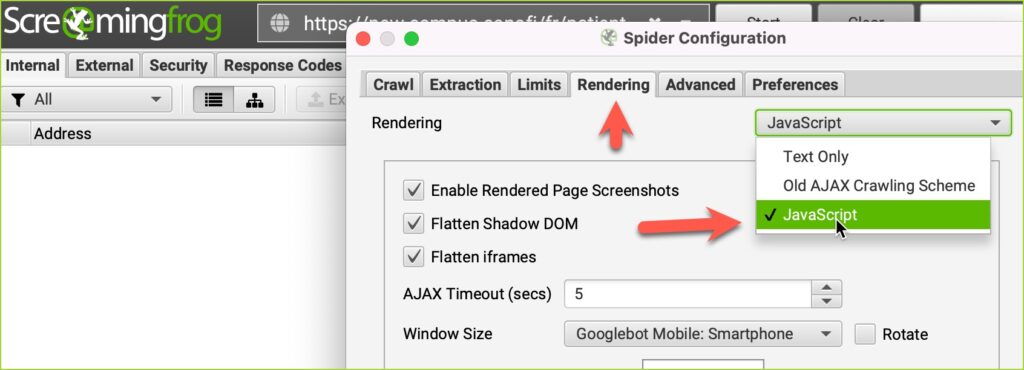
Quite often, part of the website is not rendered on the server, or perhaps the site navigation only fires up at the user request level, meaning that the robots may not see the top navigation and may only be finding the website content via HTML or XML sitemaps and internal linking routes.
Compare the n. of total pages of the two crawls: text-only and javascript. If they do not coincide then you have an area to dig in deeper, trying to find out if the part of the website not rendered at the server is appropriately indexed and without render issues. For this, the Inspect tool on GSC is invaluable.
SEO Technical Audit Efficiency Tips
Below are tips and things to look for when performing a technical SEO audit.
Don’t Overrate the Crawl
Understand that the crawl may not give you all the necessary information to optimize the site. A manual source code review is needed for more advanced cases, such as implementing advanced schema and rich snippets. Looking at the HTML for this, is a must.
Don’t Skip the Canonical Tags
Check for any canonical tags, as this will direct search engines to the right page if there are multiple versions of the same page. Canonical tags are all-important for e-commerce websites, as there are often multiple versions of a product page that search engines can index.
Always Watch Out For Duplicate Content Pages
Make sure to look for duplicate or thin content, which can hurt your SEO rankings. Do this by running a Copyscape check to ensure that the content is unique and not plagiarized. Plagiarized content will rank poorly on any of the search engines.
Manual Test on Mobile
As mentioned before, always run manual tests such as testing your website on your cell phone and other devices to ensure your website is mobile-friendly. It is a practical way to catch possible errors and issues that might otherwise fly under the radar of crawling software.
Don’t Forget About Safety and Security
Always keep your security in mind when optimizing for mobile. Whenever you make a change, be sure to check and see if it has affected the security of your website or not. Dealing with security issues can be time-consuming and expensive, so it’s best to take the time to make sure everything is secure before making any changes.
Page Performance Chumps Everything
Lastly, review page performance is a significant factor in SEO. A page that takes more than three or four seconds to load will hurt your rankings. Use tools like GTmetrix to check a page’s loading time and identify any problem areas.
A Note on International Sites
If your site has an international audience, look into hreflang tags. Hreflang tags help search engines determine which page’s version should be served to users based on their language and region. Ensuring the tags are correctly implemented is essential, as this can significantly impact your SEO rankings.
By following these steps and using the right tools, you can quickly perform a technical SEO site audit and identify any possible issues. These steps will help you optimize your website for rankings and improve your overall SEO performance.
There are many good tools in the market at the moment. Some are premium, but other ones, like Website Auditor, from SEO Powersuite, are very affordable.
Wrapping Up
Performing a technical SEO site audit is an essential step for any website that wants to grow. It helps you identify any issues hindering your site from achieving higher search engine rankings. Once you have identified the issues, you need to explain how to address them in your audit by updating your content and optimizing your website.
Commit to performing regular, thorough SEO audits to ensure that your website maintains optimization for search engine rankings.
It will help you stay ahead of the competition and maintain a high ranking in search engine results. It may seem like loads of work, but understand that some professionals and tools can help you do the job efficiently and effectively.
If you lack the budget for a robust SEO audit, you can always use the tips outlined in this article to do a basic technical SEO audit. That will help you, for sure, identify areas for improvement. Doing so will bring you closer to achieving the SEO success you strive for.
In the real world a technical audit may be tackled differently and not exactly following the steps above. It all depends on what is expected from the client. A common scenario is a sudden traffic drop where the site owner is trying to work out why it happened and how to solve it and come back to optimal levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are frequent inquiries on how to perform a technical SEO audit.
How long does a technical SEO audit take?
The time it takes to conduct a technical SEO audit may vary. It can take one day for a small website and up to two or three weeks for large projects.
It also depends on factors such as the website’s complexity, the no. of URLs to crawl and analyze, the challenge paradigm, and technology that plays a role, e.g., websites running on javascript frameworks can take longer to audit than traditional frameworks. The bigger the site, the longer it will take.
–
What is the best time to perform a technical SEO Audit?
There is no such thing as the “best time” to perform a technical audit.
SEO is an ongoing process. You won’t do it just once. Ideally, you would do it regularly in order to keep track of your website performance. For large websites, I recommend doing it at least once a year.
If you are part of an in-house SEO team, you will know that technical SEO audits constantly occur. Perhaps not comprehensively, but more ad-hoc when needed or issues appear.
–
How much is a technical SEO audit?
The cost of a technical SEO audit can vary based on the size and complexity of your website. An audit for a small website might cost around €1000, whereas an audit for a large website might cost up to €10,000 or more. If you are looking for a comprehensive technical SEO audit, it is best to budget accordingly.
–
Can I get a quality SEO audit for free?
While many free SEO audit tools are available online, they usually offer minimal information and are not comprehensive.
For a comprehensive technical SEO audit, hiring a professional who can provide you with the detailed information and analysis necessary for fully optimizing your website is advised. Or you can learn the tricks of the trade yourself.
But either way, it won’t be free. Doing it yourself may save you money but not time.
–
Is technical SEO difficult?
Technical SEO is not difficult, but it requires some knowledge and experience. You will need to be familiar with HTML and other coding languages to understand and optimize the website entirely.
However, many online tutorials and resources can help you learn the necessary skills. Once you have acquired the basic knowledge, you can optimize the website for better SEO performance.
–
What tool is best for SEO audit?
Some of the more popular tools are Sitebulb or Screaming frog, whereas on the cloud-based end there are now a large choice: Oncrawl, Botify, SEMrush, Ahrefs.
Each of these tools can provide detailed information about your website and help you identify pertinent issues that need to be addressed to improve SEO performance.
The choice will come down to the features you prefer, your budget, and previous knowledge and experience in performing and understanding of how to do a technical SEO audit.
–
What is the difference between an SEO analysis and an SEO audit?
SEO analysis is a broad overview of the current state of your website and how it performs in search engine rankings. An audit, on the other hand, is a much more detailed look at the website and its performance.
An audit will provide you with a comprehensive view of any issues that need to be updated to improve SEO performance.


 10 Quick Wins to Get More Leads From Your Website
10 Quick Wins to Get More Leads From Your Website
Leave a Reply